If you’re building a custom PC or upgrading your components, you’ve probably seen terms like “8-phase VRM” or “VRM cooling” mentioned in motherboard reviews. But what exactly is a VRM, and why should you care?
A VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) on a motherboard delivers clean, stable power to the CPU. It converts high voltage from the PSU into safe, usable voltage, ensuring performance, stability, and efficient operation.
Let’s explore what VRMs are, how they work, why they matter, and what you should look for in a good VRM design.
What is a VRM?
A VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) is an electronic circuit on your motherboard that converts high-voltage electricity from your power supply (usually 12V) into a lower voltage (like 1.2V) that your CPU and GPU can safely use.
Modern CPUs are sensitive. They require very specific, stable, and clean power delivery to function properly. Too much voltage and your chip can burn. Too little voltage and your system will crash.
So, the VRM works as a mini power plant, stepping down and regulating voltage in real-time, adapting to the CPU’s changing power needs while keeping everything stable.
How Does a VRM Work?
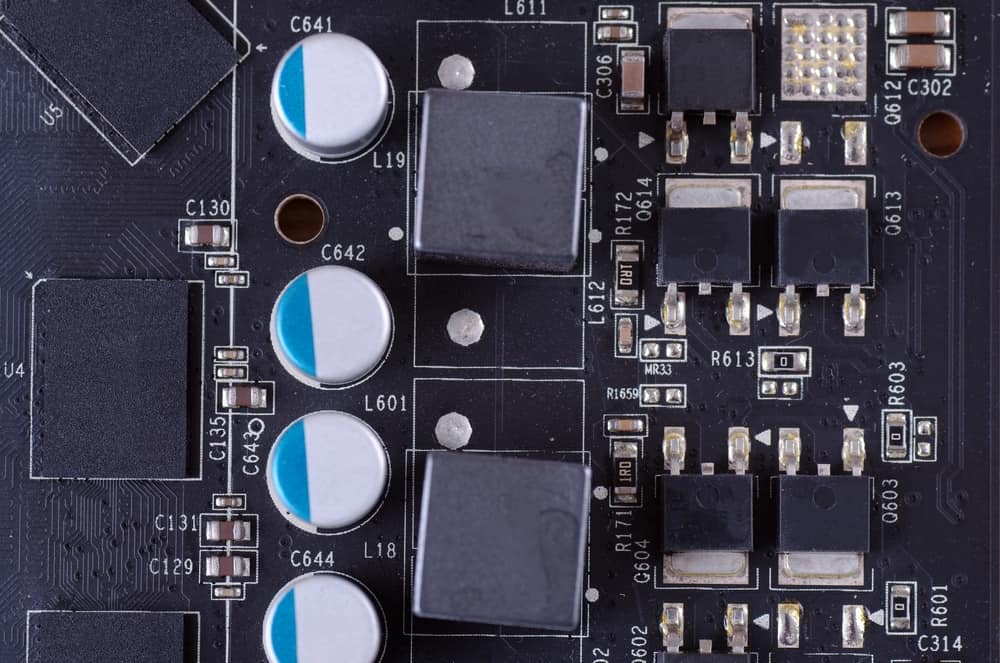
The VRM is made up of several smaller components that work together:
| Component | Function |
| MOSFETs | Control power switching |
| Chokes (Inductors) | Smooth out the power |
| Capacitors | Temporarily store and release power |
| PWM Controller | Oversees the timing and voltage delivery |
Let’s break it down simply:
- Your Power Supply Unit (PSU) sends 12 volts to the motherboard.
- The PWM controller tells the MOSFETs when to turn on and off.
- MOSFETs act like gates, allowing power to flow in pulses.
- The power goes through chokes to smooth out any noise.
- The capacitors store energy and keep the output stable.
- Finally, the CPU receives clean, regulated power at just the right voltage.
Why is VRM So Important?
A motherboard’s VRM is responsible for:
- Delivering stable power to your CPU
- Preventing voltage spikes or drops
- Supporting high power demands during gaming or productivity
- Enabling safe overclocking
- Reducing thermal load and system crashes
If the VRM fails or overheats, your CPU can throttle (slow down), crash, or even get damaged over time.
Components of VRM in Motherboard
A VRM is made up of small electrical parts that work together to send safe power to your CPU. These include MOSFETs, chokes, capacitors, and a PWM controller. Each part has a special job to make sure the power from your power supply is clean and stable. Without these parts, your computer can crash, overheat, or slow down during heavy tasks like gaming or video editing.
MOSFETs
MOSFETs are tiny switches in the VRM that control how much power is sent to the CPU. They turn on and off very fast to adjust the voltage quickly. If they don’t work well, your CPU might get too much or too little power, causing problems. Good quality MOSFETs help keep your system running smooth, especially when you’re playing games or doing heavy work on your PC.
Chokes
Chokes, also called inductors, help smooth out the power coming from the MOSFETs. They stop power spikes and noise so your CPU gets steady electricity. Think of chokes like shock absorbers for your power system. Without them, the power going to your CPU would be bumpy and unstable. Good chokes help your PC stay cool and stable, even when you’re using it for big tasks.
Capacitors
Capacitors are small parts that store and release energy quickly when needed. In a VRM, they help keep the power smooth and steady. When the CPU needs more energy fast, capacitors help deliver it without delay. They also help protect your system from sudden power changes. Quality capacitors last longer and make sure your computer stays safe and works well under pressure.
PWM Controller
The PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller is like the brain of the VRM. It decides how fast and how much power the MOSFETs should send to the CPU. It watches what the CPU needs and adjusts the power instantly. A good PWM controller keeps everything balanced, which is important for performance and energy saving. Without it, the VRM wouldn’t know how to manage power properly.
What are VRM Phases?
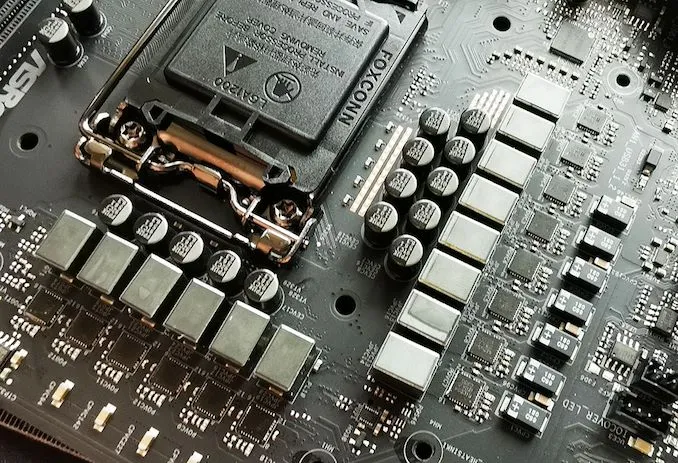
You’ll often hear terms like “4-phase VRM”, “6+2 VRM”, or “12+1 VRM” in motherboard specs. These numbers refer to how many phases or power channels the VRM uses to supply power to the CPU (and sometimes GPU or RAM).
Why More VRM Phases Matter:
- More phases = better load distribution
- Lower heat per phase
- More stable power at high loads
- Essential for high-end CPUs and overclocking
| Use Case | Recommended VRM Phases |
| Office/Browsing | 3–4 phase |
| Gaming | 6–8 phase |
| Streaming & Rendering | 8–12+ phase |
| Overclocking | 12+ phases with heatsinks |
Example:
- 4+1 phase = Budget board for low-power CPUs
- 12+2 phase = Premium board for Ryzen 9 or i9 CPUs
VRM and Heat: Why Cooling Matters
VRMs can generate a lot of heat, especially during CPU-intensive tasks. If VRMs overheat:
- The system may shut down automatically
- CPU performance will drop (thermal throttling)
- Overclocking becomes unstable or impossible
Signs of Good VRM Cooling:
- Large aluminum heatsinks over VRM section (top-left near CPU)
- Thermal pads under heatsinks
- Heatpipes or fans (on high-end boards)
- VRM temperature sensors (visible in BIOS or software)
Tip: Never buy a motherboard without checking VRM cooling quality, especially for Ryzen 9 / Core i9 CPUs.
VRMs and Overclocking
Overclocking your CPU means pushing it beyond its factory settings for more performance. However, this requires:
- Extra voltage
- Stable power delivery
- Excellent heat management
A weak VRM will not handle overclocking, no matter how good your CPU or cooler is. You’ll get crashes, blue screens, or reduced performance.
Look for:
- 10+ phase VRMs
- Digital PWM controllers
- Solid capacitors
- Reviews that mention overclocking success
VRM Quality: What to Look For in a Motherboard
1. Number of Phases
The higher, the better — especially for powerful CPUs.
2. VRM Heatsinks
Metallic heatsinks or even fans show good design.
3. Manufacturer Quality
Brands like ASUS ROG, MSI MPG, Gigabyte AORUS, and ASRock Taichi are known for solid VRM designs.
4. Online Reviews / VRM Test Charts
Check YouTube channels like Gamers Nexus or Buildzoid who do thermal + power testing.
What Are Power Phases of a Motherboard?
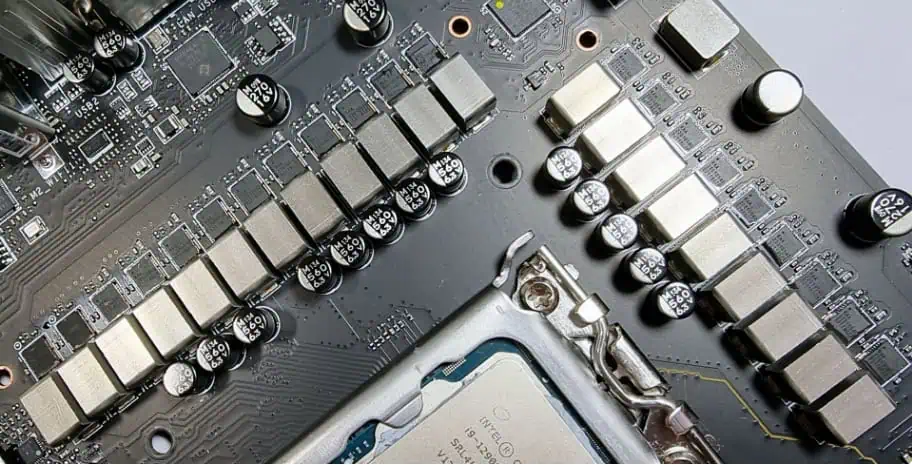
Power phases are the separate paths that a motherboard uses to deliver power to the CPU. The more phases it has, the smoother and cooler the power delivery is. This helps the CPU run better, especially during heavy tasks. Think of it like sharing a load—more hands make the job easier, and in motherboards, more phases help your system stay fast and stable.
Can the Quality of VRM Impact CPU Performance?
Yes, the quality of a VRM can seriously affect CPU performance. A strong VRM gives clean and steady power, helping your CPU run smoothly even under pressure. If the VRM is weak, your computer might lag, freeze, or shut down during games or work. A good VRM means better performance, fewer problems, and a longer life for your CPU and overall system.
How Can You Tell If Your VRM Is up to the Task?
To check if your VRM is good enough, look at the motherboard specs. A higher number of power phases and big metal heatsinks are good signs. Also, check trusted reviews or YouTube teardowns. If you’re using a high-end CPU or planning to overclock, choose a motherboard with a solid VRM design. A weak VRM may lead to overheating, slowdowns, or system crashes.
Why Good VRMs Are Required for Overclocking?
Overclocking means pushing your CPU beyond its normal speed, which needs extra power. A good VRM provides that power without overheating or failing. It keeps your system stable and safe while giving you better performance. Weak VRMs can cause crashes, poor results, or even damage your CPU. So, if you plan to overclock, make sure your motherboard has a strong VRM with proper cooling.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is VRM Important for Gaming?
Yes, VRM matters in gaming because it helps your CPU get stable power. A strong VRM means smoother gameplay and fewer lags or crashes.
What is VRAM in a Motherboard?
VRAM isn’t on the motherboard. It’s video memory found in your graphics card, not the VRM, which controls power for your CPU, not graphics.
Are More VRM Phases Better?
Yes, more VRM phases give smoother and cooler power to your CPU. It helps with performance, stability, and is better for gaming and overclocking.
Does Motherboard VRM Affect Performance?
Absolutely! A good VRM helps your CPU run at full power. Poor VRMs can cause slowdowns, heat issues, or even system crashes during heavy use.
How to Tell if VRM is Bad?
If your PC shuts down, gets hot, or crashes during tasks, your VRM might be weak or overheating. Check BIOS or use system monitor tools.
What Are the Advantages of VRM?
VRMs deliver clean power to your CPU, improving stability, performance, and allowing overclocking. They protect your system and keep everything running smoothly under load.
Final Thoughts
Your motherboard’s VRM might not get as much attention as the CPU or GPU, but it plays a critical role in your system’s performance, especially for gaming, multitasking, or overclocking.
When buying a new motherboard:
- Always check VRM phase count
- Look at cooling solutions
- Match VRM quality to your CPU’s power needs